ABOUT GCAN
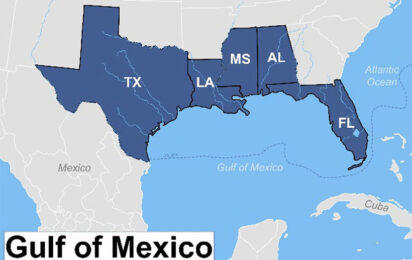
GCAN, hosted by the Gulf of Mexico Coastal Ocean Observing System (GCOOS), works directly with scientists, resource managers, stakeholders and educators to facilitate, synthesize and communicate the state of coastal and ocean acidification science in the Gulf of Mexico region. GCAN also collaborates with other regional efforts across the U.S. and Caribbean as well as the NOAA’s Ocean Acidification Program (OAP) and other federal resource managers.

Newsletter SIGN UP
Ocean acidification (OA) occurs when oceans absorb excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, making the pH of seawater lower, or more acidic. This chemistry change can make it more difficult for marine life to form and maintain calcium-rich structures like the skeletons of corals or the shells of many commercially important shellfish. (Video by NOAA’s National Ocean Service)
GCAN News and Information
New Gulf of Mexico Initiative Seeks to Address Ocean Acidification Across International Borders
Scientists from the U.S., Mexico and Cuba are working together to exchange information and begin development of a new tri-national initiative designed to address the socioeconomic impacts of ocean acidification (OA) in the Gulf of Mexico based on common needs across nations.

Have a question about GCAN? Wondering whether you should join?
Interested in becoming a GCAN Member?
Looking for Ocean Acidification Data?
Tampa Bay LOBO
Tampa Bay has successfully recovered from decades of severe eutrophication through community efforts to reduce nitrogen loads, improve water quality, and restore and protect thousands of acres of seagrass, mangrove forest and salt marsh.
These research activities are enhanced by the deployment of a Land/Ocean Biogeochemical Observatory (LOBO), Ocean Carbon System (OCS) in partnership with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), and in collaboration with the USF Center for Maritime and Port Studies and the Tampa Bay Physical Oceanographic Real Time System to provide real-time, high resolution water quality data through this interactive website.
The Ocean and Coastal Acidification Network
GCAN is just one of the regional coastal acidification networks in the U.S. working closely with NOAA’s Ocean Acidification Program
GCAN Collaborations
GCAN is a proud member of the Ocean Acidification Alliance, an international alliance to combat ocean acidification.
- NOAA’s Ocean Acidification Program (OAP)
- Gulf Shellfish Institute (GSI)
- NOAA’s SeaGrant
- Florida Shellfish Aquaculture Association (FSAA)
- Ocean Conservancy
- The Nature Conservancy: Shellfish Growers Climate Coalition
- Flower Garden Banks National Marine Sanctuary (FGBNMS)
- Texas A&M University
- Auburn University
- Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS)